前言
SpringCloud中的NamedContextFactory可以创建一个子容器(child context),每个子容器可以通过Specification定义Bean。一般用于不同微服务的客户端使用不同的子上下文进行配置,ribbon和feign的配置隔离都是依赖这个抽象类来实现的。
举个简单的例子,在一套微服务的系统中,服务A是一个报表服务需要查询并统计大量数据,响应时间会很慢,而服务B是一个简单的订单查询服务,响应会很快,很显然两个服务的响应超时时间要求是不同的。所以我们针对不同的微服务使用不同的ApplicationContext。
原理
NamedContextFactory的核心是getInstance方法
public <T> T getInstance(String name, Class<T> type) {
// 根据name获取子容器
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = getContext(name);
try {
// 根据类型从子容器中获取bean
return context.getBean(type);
}
catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException e) {
// ignore
}
return null;
}逻辑很简单就是根据name获取子容器,然后根据类型获取子容器中的bean
重点看一下getContext方法
protected AnnotationConfigApplicationContext getContext(String name) {
if (!this.contexts.containsKey(name)) {
synchronized (this.contexts) {
if (!this.contexts.containsKey(name)) {
this.contexts.put(name, createContext(name));
}
}
}
return this.contexts.get(name);
}
protected AnnotationConfigApplicationContext createContext(String name) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext();
// 找对应name的配置类
if (this.configurations.containsKey(name)) {
for (Class<?> configuration : this.configurations.get(name)
.getConfiguration()) {
context.register(configuration);
}
}
// 找default开头的配置类
for (Map.Entry<String, C> entry : this.configurations.entrySet()) {
if (entry.getKey().startsWith("default.")) {
for (Class<?> configuration : entry.getValue().getConfiguration()) {
context.register(configuration);
}
}
}
// 注册默认的配置类
context.register(PropertyPlaceholderAutoConfiguration.class,
this.defaultConfigType);
context.getEnvironment().getPropertySources().addFirst(new MapPropertySource(
this.propertySourceName,
Collections.<String, Object>singletonMap(this.propertyName, name)));
if (this.parent != null) {
// Uses Environment from parent as well as beans
context.setParent(this.parent);
// jdk11 issue
// https://github.com/spring-cloud/spring-cloud-netflix/issues/3101
context.setClassLoader(this.parent.getClassLoader());
}
context.setDisplayName(generateDisplayName(name));
context.refresh();
return context;
}根据name从Map中去取,如果没有就创建子容器,在创建的时候,先找相同name的配置类,如果有就注册,然后找default.开头的配置类,如果有就注册,然后子容器中注册PropertyPlaceholderAutoConfiguration以及defaultConfigType,最后设置父容器完成初始化。其中PropertyPlaceholderAutoConfiguration是用于解析Bean或@Value中的占位符。
简单测试
先贴一下pom文件,要注意springboot和springcloud的版本是有对应关系的
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.7.8</version>
<relativePath/>
</parent>
<groupId>org.example</groupId>
<artifactId>named-context-factory-demo</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<properties>
<maven.compiler.source>11</maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>11</maven.compiler.target>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-context</artifactId>
<version>3.1.0</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<configuration>
<excludes>
<exclude>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
</exclude>
</excludes>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>为了展示代码方便我全部放到一个测试类中,可以直接拿来Debug
package org.example;
import lombok.ToString;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.cloud.context.named.NamedContextFactory;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.core.env.Environment;
import java.util.List;
@SpringBootTest
public class NamedContextFactoryTest {
private static final String PROPERTY_NAME = "custom.client.name";
@Test
public void context() {
// 创建 parent context
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext parent = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext();
// parent context 的 Bean,可以被子容器继承
parent.register(ParentConfig.class);
// 初始化 parent
parent.refresh();
// 创建子容器
CustomSpecification aServiceSpec = new CustomSpecification("AService", new Class[]{AServiceConfig.class});
CustomSpecification bServiceSpec = new CustomSpecification("BService", new Class[]{BServiceConfig.class});
// 默认使用配置 commonConfig
CustomNamedContextFactory customNamedContextFactory = new CustomNamedContextFactory(CommonConfig.class);
// SpringBoot 中无需手动设置,会自动注入 parent
customNamedContextFactory.setApplicationContext(parent);
// 添加子容器到父容器中
customNamedContextFactory.setConfigurations(List.of(aServiceSpec, bServiceSpec));
// 准备工作完成,现在开始通过 NamedContextFactory get Bean
ParentBean aParentBean = customNamedContextFactory.getInstance("AService", ParentBean.class);
CommonBean aCommonBean = customNamedContextFactory.getInstance("AService", CommonBean.class);
AServiceBean aServiceBean = customNamedContextFactory.getInstance("AService", AServiceBean.class);
ParentBean bParentBean = customNamedContextFactory.getInstance("BService", ParentBean.class);
CommonBean bCommonBean = customNamedContextFactory.getInstance("BService", CommonBean.class);
BServiceBean bServiceBean = customNamedContextFactory.getInstance("BService", BServiceBean.class);
// 获取到相同的parent bean
Assertions.assertEquals(aParentBean, bParentBean);
// 获取到不同的common bean
Assertions.assertNotEquals(aCommonBean, bCommonBean);
// 获取到各自的service bean
Assertions.assertNotNull(aServiceBean);
Assertions.assertNotNull(bServiceBean);
System.out.println(aParentBean);
System.out.println(bParentBean);
System.out.println(aCommonBean);
System.out.println(bCommonBean);
System.out.println(aServiceBean);
System.out.println(bServiceBean);
}
static class CustomNamedContextFactory extends NamedContextFactory<CustomSpecification> {
public CustomNamedContextFactory(Class<?> defaultConfigType) {
super(defaultConfigType, "custom", PROPERTY_NAME);
}
}
static class CustomSpecification implements NamedContextFactory.Specification {
private String name;
private Class<?>[] configuration;
public CustomSpecification(String name, Class<?>[] configuration) {
this.name = name;
this.configuration = configuration;
}
@Override
public String getName() {
return name;
}
@Override
public Class<?>[] getConfiguration() {
return configuration;
}
}
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
static class ParentConfig {
@Bean
public ParentBean parentBean() {
return new ParentBean();
}
}
static class ParentBean {
}
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
static class CommonConfig {
@Bean
CommonBean commonBean(Environment environment, ParentBean parentBean) {
//在创建 NamedContextFactory 里面的子 ApplicationContext 的时候,会指定 name,这个 name 对应的属性 key 即 PROPERTY_NAME
return new CommonBean(environment.getProperty(PROPERTY_NAME), parentBean);
}
}
@ToString
static class CommonBean {
private final String name;
private final ParentBean parentBean;
public CommonBean(String name, ParentBean parentBean) {
this.name = name;
this.parentBean = parentBean;
}
}
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
static class AServiceConfig {
@Bean
public AServiceBean aServiceBean(CommonBean commonBean) {
return new AServiceBean(commonBean);
}
}
@ToString
static class AServiceBean {
private final CommonBean commonBean;
public AServiceBean(CommonBean commonBean) {
this.commonBean = commonBean;
}
}
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
static class BServiceConfig {
@Bean
public BServiceBean bServiceBean(CommonBean commonBean) {
return new BServiceBean(commonBean);
}
}
@ToString
static class BServiceBean {
private final CommonBean commonBean;
public BServiceBean(CommonBean commonBean) {
this.commonBean = commonBean;
}
}
}
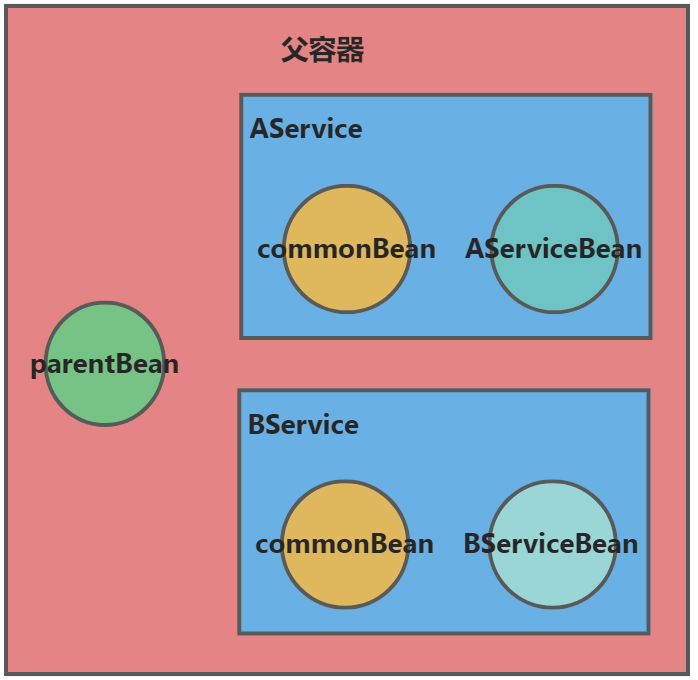
输出结果如下:
org.example.NamedContextFactoryTest$ParentBean@6fc6deb7
org.example.NamedContextFactoryTest$ParentBean@6fc6deb7
NamedContextFactoryTest.CommonBean(name=AService, parentBean=org.example.NamedContextFactoryTest$ParentBean@6fc6deb7)
NamedContextFactoryTest.CommonBean(name=BService, parentBean=org.example.NamedContextFactoryTest$ParentBean@6fc6deb7)
NamedContextFactoryTest.AServiceBean(commonBean=NamedContextFactoryTest.CommonBean(name=AService, parentBean=org.example.NamedContextFactoryTest$ParentBean@6fc6deb7))
NamedContextFactoryTest.BServiceBean(commonBean=NamedContextFactoryTest.CommonBean(name=BService, parentBean=org.example.NamedContextFactoryTest$ParentBean@6fc6deb7))如图所示在同一个NamedContextFactory中,父容器中有一个parentBean,两个子容器有自己的bean,子容器可以访问到父容器的上下文,并且访问到的是同一个实例,子容器之间是相互隔离的。