前言
我们都知道,spring 已经成为了java实际上的基础。大多数时候,我们在开发过程中更多的是面向spring的编程,那么spring bean 的生命周期,基本也出成为了面试的必考项。本文,对照源码把spring bean的生命周期梳理下。
version: spring boot 2.6.3
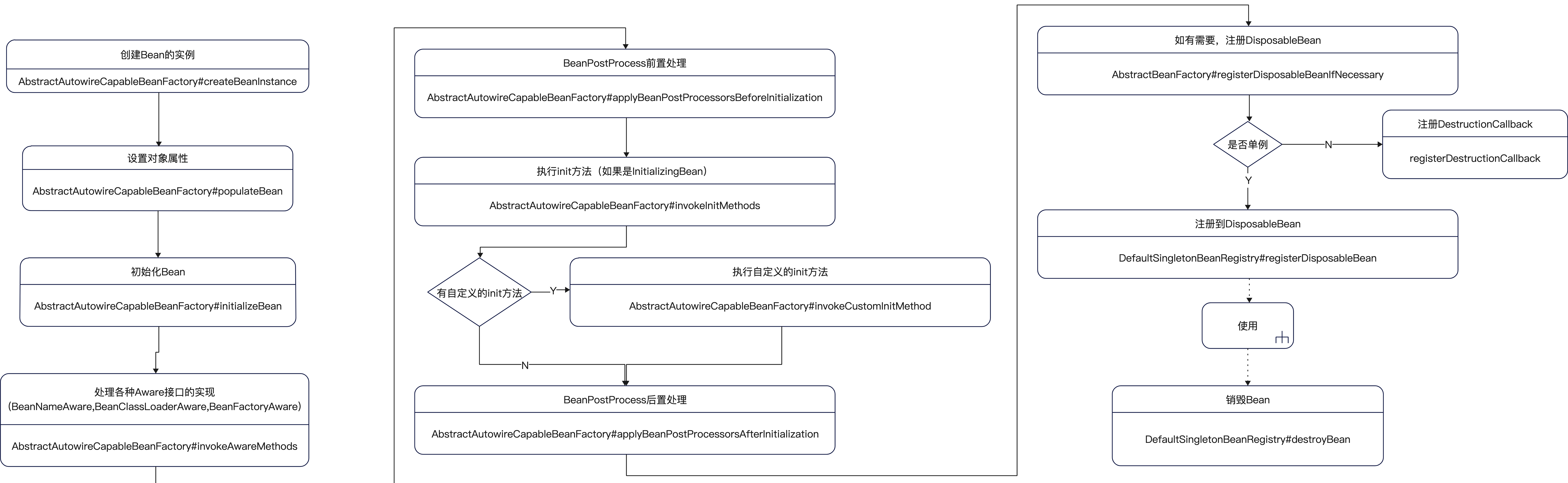
我们将bean的生命周期,梳理得到如下图
1.spring boot 执行run之后,开始进行各种准备工作,这个内容可以在 SpringApplication#run 中看到。
在prepareContext 这个环节,对spirng boot的启动类进行处理,包括启动类上的注解处理,对context进行装配初始化赋值等等,例如beanFactory,beanFactoryPostProcessor
下面进入refreshContext这个环节,这里是对bean处理的主要环节。代码位于 AbstractApplicationContext#refresh 在这里,我们可以看到bean的整个装配过程。
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) {
StartupStep contextRefresh = this.applicationStartup.start("spring.context.refresh");
// Prepare this context for refreshing.
prepareRefresh();
// Tell the subclass to refresh the internal bean factory.
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory();
// Prepare the bean factory for use in this context.
prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);
try {
// Allows post-processing of the bean factory in context subclasses.
postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
StartupStep beanPostProcess = this.applicationStartup.start("spring.context.beans.post-process");
// Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context.
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// Register bean processors that intercept bean creation.
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);
beanPostProcess.end();
// Initialize message source for this context.
initMessageSource();
// Initialize event multicaster for this context.
initApplicationEventMulticaster();
// Initialize other special beans in specific context subclasses.
onRefresh();
// Check for listener beans and register them.
registerListeners();
// Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons.
finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);
// Last step: publish corresponding event.
finishRefresh();
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - " +
"cancelling refresh attempt: " + ex);
}
// Destroy already created singletons to avoid dangling resources.
destroyBeans();
// Reset 'active' flag.
cancelRefresh(ex);
// Propagate exception to caller.
throw ex;
}
finally {
// Reset common introspection caches in Spring's core, since we
// might not ever need metadata for singleton beans anymore...
resetCommonCaches();
contextRefresh.end();
}
}
}beanDefinition的处理主要在 invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors 这一步中。追溯代码到 PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate#invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors 在这一步中,通过ConfigurationClassPostProcessor#postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry 来处理beanDefinition的注册,代码追溯 ConfigurationClassParser#parse-> ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner#doScan ,在这个doScan方法中,完成了对符合实例化条件的class的beanDefinition注册。
在beanDefinition完成注册之后,已经具备了实例化bean的物料。下面就可以开始进行实例化。主要代码依旧在 PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate#finishBeanFactoryInitialization 由代码可以看到,spring讲需要实例化的class 分成了三个优先级
- priorityOrderedPostProcessors PriorityOrdered 类型的
- orderedPostProcessorNames Ordered类型的
- nonOrderedPostProcessorNames
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors 中,主要完成了beanDefinition注册以及BeanFactoryPostProcessor实现类的实例化。而普通单例bean的实例化主要在finishBeanFactoryInitialization中去完成。
我们通过代码追溯,可以看到 bean的实例化过程,主要是在 AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory#createBean 完成的。
主要步骤如下
我们来写一个类来测试一下
@Component
public class BeanComponent implements ApplicationContextAware, BeanNameAware, BeanFactoryAware, BeanFactoryPostProcessor, BeanPostProcessor, EnvironmentAware, InitializingBean, DisposableBean {
@Override
public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("ApplicationContextAware-> setApplicationContext");
}
@Override
public void setBeanName(String name) {
System.out.println("BeanNameAware-> setBeanName");
}
@Override
public void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("BeanFactoryPostProcessor-> postProcessBeanFactory");
}
@Override
public void setEnvironment(Environment environment) {
System.out.println("EnvironmentAware-> setEnvironment");
}
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
System.out.println("InitializingBean-> afterPropertiesSet");
}
@Override
public void destroy() throws Exception {
System.out.println("DisposableBean-> destroy");
}
@Override
public void setBeanFactory(BeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("BeanFactoryAware-> setBeanFactory");
}
}
打印的内容如下
BeanNameAware-> setBeanName
BeanFactoryAware-> setBeanFactory
EnvironmentAware-> setEnvironment
ApplicationContextAware-> setApplicationContext
InitializingBean-> afterPropertiesSet
BeanFactoryPostProcessor-> postProcessBeanFactory
Disconnected from the target VM, address: '127.0.0.1:58617', transport: 'socket'
2022-03-18 19:25:19.190 INFO 39144 --- [ main] ms.bean.BeanApp : Started BeanApp in 1324.59 seconds (JVM running for 1325.557)
DisposableBean-> destroy这样,可以比较直观的看到bean生命周期的一个顺序。
根据上面所述,我们可以根据bean的生命周期的执行,在其中添加一些我们的处理逻辑。
如果是要动态创建bean 并且被其他的bean依赖注入,应该使用BeanFactoryPostProcessor的实现类来做,这样,才能保证这个bean在最先执行。
@RequiredArgsConstructor
@Configuration
public class BeanConfiguration implements BeanFactoryPostProcessor {
@Override
public void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException {
GenericApplicationContext genericApplicationContext = new GenericApplicationContext((DefaultListableBeanFactory) beanFactory);
genericApplicationContext.registerBean(UserComponent.class);
}
}以上,就是跟着源码所见的spring bean的生命周期梳理。
